Once upon a time, way back before 1961, there actually were two sets of atomic masses (though everybody called them atomic weights then). One scale was used by physicists; the other by chemists. Both were based on weights compared to Oxygen, rather than Hydrogen. Oxygen was used because it combines with a lot of things to form oxides. This made it a better choice as a standard because of the ease of chemical analysis. Oxygen was set to have an atomic mass of 16, which was just about 16 times as heavy as Hydrogen being 1. Unfortunately, Chemists picked naturally occurring Oxygen, which is a mixture of isotopes of Oxygen-16, Oxygen-17, and Oxygen-18. After all when you made an oxide of an element you would do so in naturally occurring oxygen. Physicists picked the pure isotope Oxygen-16, because they tended to make their measurements on the basis of mass spectrometry.
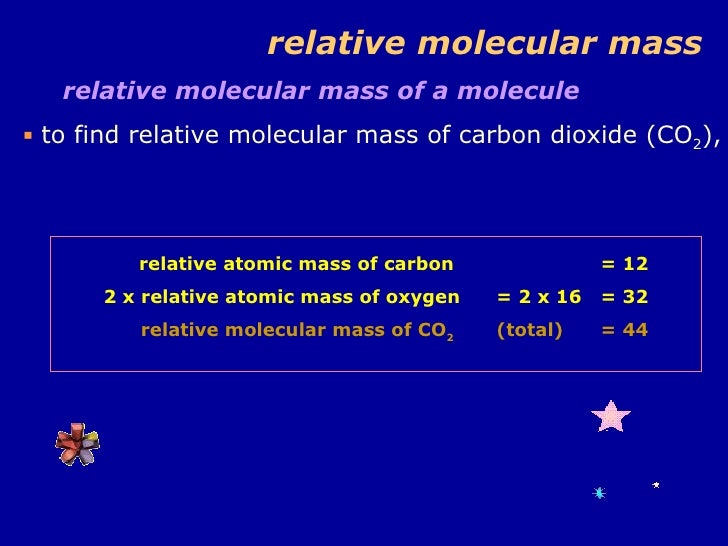
Atomic Mass Of Carbon Dioxide
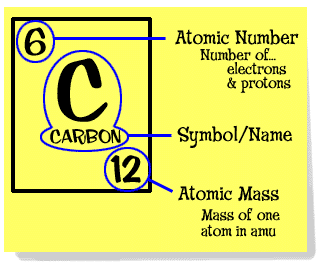
By definition, 1 atomic mass or 1amu is the mass equal to 1/12th of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 isotope. So, atomic mass of carbon is 12 amu or 12u. Plus, Carbon-12’s atomic mass could be measured particularly accurately compared to the other elements on the periodic table. So the Atomic Mass of Carbon-12 is defined to be 12 exactly and all other atomic, molecular and formula masses are referred to this standard. Question and answer according to the image the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011, How is atomic mass of mass of carbon, or any other element, determined The atomic mass of carbon is determined by: adding the number of protons and the number of neutrons together. Atomic mass of Carbon Carbon is present in the 14th group of elements in the Periodic Table. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the atomic mass is 12.01gmol-1. Carbon-12 as the standard, setting its atomic mass at 12. Panchatantra stories in english free pdf.
Atomic Mass Of Carbon Rounded
Though the ratio of any two atom’s masses was the same on either scale, it was horribly confusing, so in 1961, a compromise was reached. Instead of using either Hydrogen, or Oxygen as the standard, the isotope of Carbon with 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus (Carbon-12) was given a mass of exactly 12. It was a good choice, since it was in between the two previously used standards, and meant that nothing had to change too much. Plus, Carbon-12’s atomic mass could be measured particularly accurately compared to the other elements on the periodic table.
Atomic Mass Of Carbon-12
So the Atomic Mass of Carbon-12 is defined to be 12 exactly and all other atomic, molecular and formula masses are referred to this standard.